반응형
* 인접 행렬
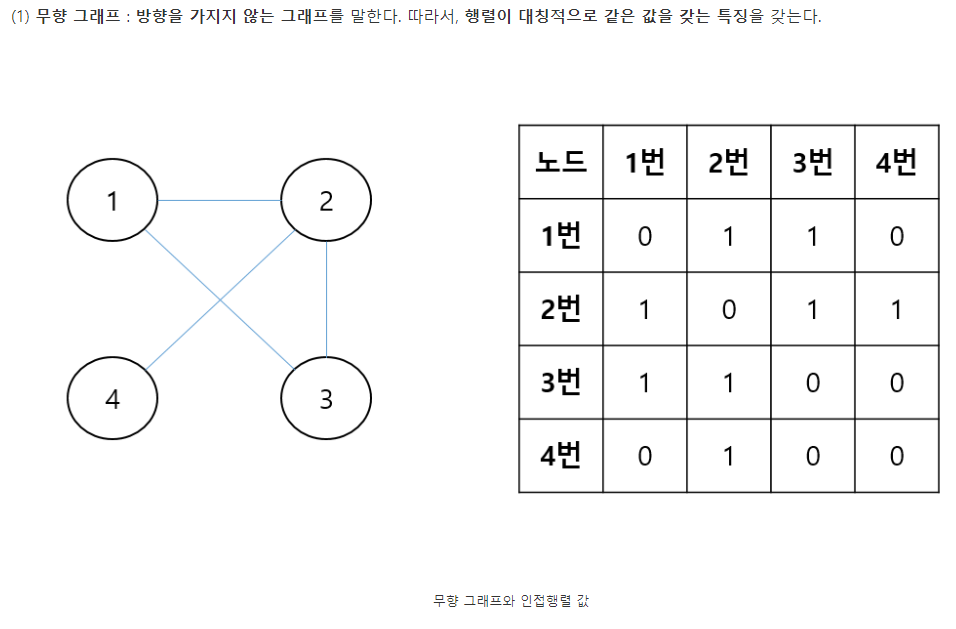
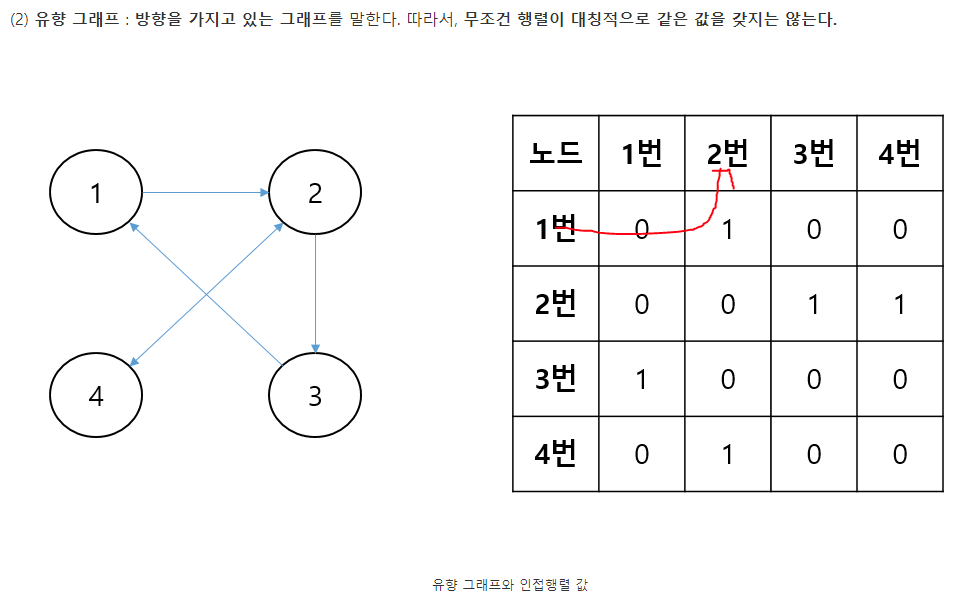
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
정점, 간선의 개수 이후
(노드, 노드, 비용)이 주어진 경우
5 6
5 1 1
1 2 2
1 3 3
2 3 4
2 4 5
3 4 6
*/
public class Graph {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// V = 정점의 개수, E = 간선의 개수.
int V = sc.nextInt();
int E = sc.nextInt();
// 2차원 배열(인접 행렬)을 만든다.
// 인덱스의 번호 = 노드의 번호 이기 때문에, 2차원 배열의 크기를 임의로 1 늘려서 정의한다(스킬).
int[][] graph = new int[V + 1][V + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int row = sc.nextInt();
int col = sc.nextInt();
int cost = sc.nextInt();
graph[row][col] = cost;
// 만일, 무방향 그래프라면 반대의 상황도 추가해 준다.
// graph[col][row] = cost;
}
// 인접 행렬 출력
for(int i = 1; i < V + 1; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j < V + 1; j++) {
System.out.print(graph[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
sc.close();
}
}
* 인접 리스트
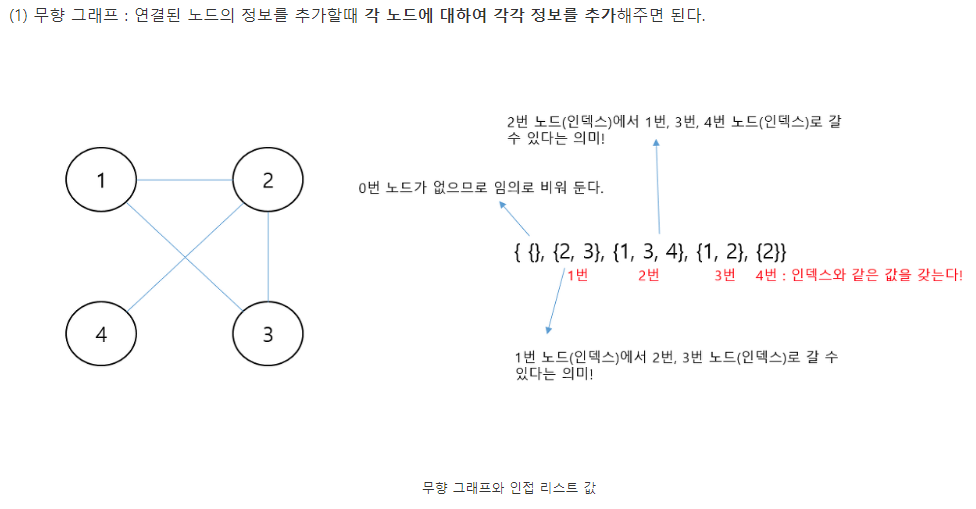
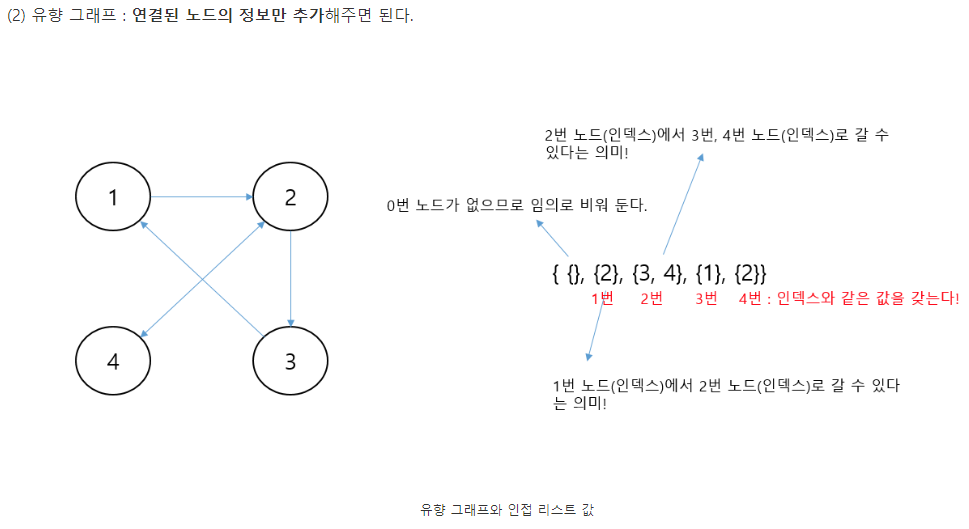
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
정점, 간선의 개수 이후
(노드, 노드, 비용)이 주어진 경우
5 6
5 1 1
1 2 2
1 3 3
2 3 4
2 4 5
3 4 6
*/
public class Graph {
// 노드와 비용을 포함하는 객체를 미리 만들어준다.
static public class Node {
int end; // 연결되는 정점
int cost; // 비용
Node(int end, int cost) {
this.end = end;
this.cost = cost;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// V = 정점의 개수, E = 간선의 개수.
int V = sc.nextInt();
int E = sc.nextInt();
// 1차원 리스트를 만든다.
// 인덱스의 번호 = 노드의 번호 이기 때문에, 1차원 리스트의 크기를 임의로 1 늘려서 정의한다(스킬).
List<ArrayList<Node>> graph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Node>>();
for (int i = 0; i < V + 1; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<Node>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
int cost = sc.nextInt();
graph.get(a).add(new Node(b, cost));
// 만일, 무향 그래프라면 반대의 상황도 추가해 준다.
// graph.get(b).add(new Node(a, cost));
}
// 인접 행렬 출력
System.out.println(graph);
sc.close();
}
반응형
'알고리즘 PS > 알고리즘 일반' 카테고리의 다른 글
| PS 풀이결과 표기 방법 (◎ / ○ / △ ) (0) | 2022.12.22 |
|---|---|
| 닥익스트라 최단경로 알고리즘 (1) | 2022.10.13 |
| 플러드 필(Flood Fill) 알고리즘 (0) | 2022.10.01 |
| 이분탐색 알고리즘(Upper Bound, Lower Bound) (0) | 2022.09.22 |
| Java의 자료구조 사용법 (0) | 2022.09.22 |


댓글