

https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/16236
16236번: 아기 상어
N×N 크기의 공간에 물고기 M마리와 아기 상어 1마리가 있다. 공간은 1×1 크기의 정사각형 칸으로 나누어져 있다. 한 칸에는 물고기가 최대 1마리 존재한다. 아기 상어와 물고기는 모두 크기를 가
www.acmicpc.net
<문제 해석>
맵의 크기는 N * N
물고기 M마리와 아기상어 1마리
아기상어와 물고기는 자연수로 표시된 크기를 가진다.
처음에 아기상어의 크기는 2이고, 1초에 상하좌우로 한칸씩 움직일 수 있다.
* 아기상어 이동조건
1. 자신의 크기보다 큰 물고기가 있는 칸은 지나갈 수 없다.
2. 자기보다 크기가 작은 물고기만 먹을 수 있다.
3. 같은 물고기가 있는 칸은 먹을 수는 없고 지나갈 수만 있다.
4. 먹을 수 있는 물고기가 여러마리면 가장 가까운 물고기를 먹으러 간다.
5. 거리가 가까운 물고기가 많다면 가장 위에, 가장 왼쪽에 있는 물고기를 먹는다.
* 종료조건
1. 더 이상 먹을 수 있는 물고기가 없으면 엄마상어에게 도움을 청한다.
2. 엄마상어에게 호출하면서 지나온 시간을 출력한다.
물고기를 먹으면 숫자를 0으로 바꾸자.
1. BFS탐색을 물고기를 먹을 때까지 계속 한다.
- 방문배열 체크
- 이동거리 저장
2. 물고기를 먹으면 그 자리에 아기상어를 이동한다.
3. 그 자리에서 다음 물고기를 먹을 때까지 탐색을 시작한다.
- 방문배열 초기화
<풀이>
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.lang.Comparable;
public class Main {
static int N;
static int map[][];
static boolean visited[][];
static int dx[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}; // 상하좌우 4방향
static int dy[] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
//static int dx[] = {-1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1}; // 상하좌우 & 대각선 8방향
//static int dy[] = {0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1};
//static int distance = 0;
//static boolean flag = true;
static int count_eat = 0;
static int shark_size = 2;
static int total_dist = 0;
class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
int x, y, size, dist;
Node (int x, int y, int size, int dist) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.size = size;
this.dist = dist;
}
// 1. 이동거리가 가장 적은 순으로
// 2. 이동거리가 같으면 가장 위의 물고기 순으로
// 3. 그 다음은 왼쪽의 물고기 순으로 오름차순 정렬
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
if (this.dist != o.dist) return this.dist - o.dist;
else if (this.x != o.x) return this.x - o.x;
else return this.y - o.y;
}
}
void printMap() {
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<N; j++) {
System.out.print(map[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("---------------");
}
Node BFS(Node start) {
Queue<Node> Q = new LinkedList<>();
ArrayList<Node> list = new ArrayList<>();
Q.add(start);
visited[start.x][start.y] = true; // 시작점 방문처리
while (!Q.isEmpty()) {
Node now = Q.poll();
for (int i=0; i<4; i++) {
int nx = now.x + dx[i];
int ny = now.y + dy[i];
// 가지치기
if (nx<0 || nx>=N || ny<0 || ny>=N) continue; // 맴 범위를 벗어나면 패스
if (visited[nx][ny]) continue; // 방문한 곳이면 패스
if (now.size < map[nx][ny]) continue; // 큰 물고기면 패스
// 큐에 넣기
visited[nx][ny] = true; // 방문처리
Q.add(new Node(nx, ny, now.size, now.dist+1));
// 먹을 수 있는 물고기 발견하면 일단 list에 넣기
if (map[nx][ny] != 0 && now.size > map[nx][ny]) { // 0이 아니고, 상어보다 작으면
list.add(new Node(nx, ny, now.size, now.dist+1));
}
}
}
// 먹을 물고기 위치 정하기
Collections.sort(list);
return list.get(0);
}
boolean foundSmallFish(int size) {
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<N; j++) {
if (map[i][j] == 0 || map[i][j] == 9) continue;
if (map[i][j] < size) return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void Solve() {
while (foundSmallFish(shark_size)) { // 작은 물고기가 남아있으면 계속 탐색
// 아기상어 위치 찾기
loop:
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<N; j++) {
if (map[i][j] == 9) {
visited = new boolean[N][N]; // 방문배열 초기화
//System.out.println("shark : BFS("+i+", "+j+", "+shark_size+", "+total_dist+")");
Node move = BFS(new Node(i, j, shark_size, total_dist));
// 물고기를 먹고 그 위치로 아기상어 위치 이동
map[i][j] = 0;
map[move.x][move.y] = 9;
count_eat++;
if (count_eat >= move.size) {
shark_size = move.size+1;
count_eat = 0;
} else {
shark_size = move.size;
}
total_dist = move.dist;
//printMap();
break loop;
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(total_dist);
}
void inputData() throws Exception {
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader);
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());//열
//M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());//행
map = new int[N][N];
//visited = new boolean[N][N];
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
//String str = br.readLine();
for (int j=0; j<N; j++) {
map[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
//map[i][j] = str.charAt(j);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Main m = new Main();
m.inputData(); // 입력 받는 부분
m.Solve();// 여기서부터 작성
}
}
<풀이 수정>
런타임 에러가 발생한다. 백준 게시판을 살펴보다가 비슷한 질문이 있길래 봤더니 반례가 있었다.
2
3 9
1 3
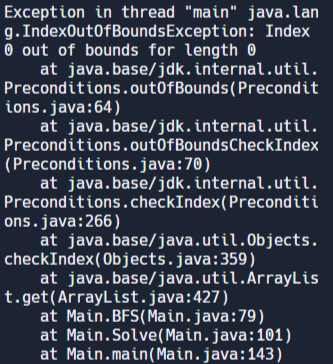
ArrayList에 값이 없는 경우를 예외처리 해줘야 하는 걸 누락했다.
<다시 풀기>
1. 물고기를 먹고 그 위치에 상어위치로 map[nx][ny] = 9를 해줬는데 이게 꼬인 것 같다.
2. 상어 위치는 shark_x, shark_y 전역변수로 가지고 있으면 되고 map[nx][ny] = 0으로 해줬더니 100%로 통과했다.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.lang.Comparable;
public class Main {
static int N;
static int map[][];
static boolean visited[][];
static int dx[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}; // 상하좌우 4방향
static int dy[] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
static int count_eat = 0;
static int shark_size = 2;
static int total_dist = 0;
static int shark_x = 0, shark_y = 0;
class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
int x, y, size, dist;
Node (int x, int y, int size, int dist) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.size = size;
this.dist = dist;
}
// 1. 이동거리가 가장 적은 순으로
// 2. 이동거리가 같으면 가장 위의 물고기 순으로
// 3. 그 다음은 왼쪽의 물고기 순으로 오름차순 정렬
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
if (this.dist != o.dist) return this.dist - o.dist;
else if (this.x != o.x) return this.x - o.x;
else return this.y - o.y;
}
}
void printMap() {
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<N; j++) {
System.out.print(map[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("---------------");
}
Node BFS(Node start) {
Queue<Node> Q = new LinkedList<>();
ArrayList<Node> list = new ArrayList<>();
Q.add(start);
visited[start.x][start.y] = true; // 시작점 방문처리
while (!Q.isEmpty()) {
Node now = Q.poll();
for (int i=0; i<4; i++) {
int nx = now.x + dx[i];
int ny = now.y + dy[i];
// 가지치기
if (nx<0 || nx>=N || ny<0 || ny>=N) continue; // 맴 범위를 벗어나면 패스
if (visited[nx][ny]) continue; // 방문한 곳이면 패스
if (now.size < map[nx][ny]) continue; // 큰 물고기면 패스
// 큐에 넣기
visited[nx][ny] = true; // 방문처리
Q.add(new Node(nx, ny, now.size, now.dist+1));
// 먹을 수 있는 물고기 발견하면 일단 list에 넣기
if (map[nx][ny] != 0 && now.size > map[nx][ny]) { // 0이 아니고, 상어보다 작으면
list.add(new Node(nx, ny, now.size, now.dist+1));
}
}
}
// 먹을 물고기 위치 정하기
Collections.sort(list);
if (!list.isEmpty()) return list.get(0);
else return null;
}
boolean foundSmallFish(int size) {
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<N; j++) {
if (map[i][j] == 0 || map[i][j] == 9) continue;
if (map[i][j] < size) return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void Solve() {
// 아기상어 첫 위치 찾기
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<N; j++) {
if (map[i][j] == 9) {
shark_x = i;
shark_y = j;
map[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
// 작은 물고기가 남아있으면 계속 탐색
while (foundSmallFish(shark_size)) {
visited = new boolean[N][N]; // 방문배열 초기화
Node move = BFS(new Node(shark_x, shark_y, shark_size, total_dist));
// 물고기를 못 찾았으면
if (move == null) {
System.out.println(total_dist);
return;
}
// 물고기를 찾았으면
// 상어위치를 물고기 위치로 저장
shark_x = move.x;
shark_y = move.y;
// 물고기 위치는 0으로 갱신
map[move.x][move.y] = 0;
count_eat++; // 물고기 먹은 수 증가
if (count_eat == move.size) { // 먹은 수와 상어사이즈가 같으면
shark_size = move.size+1; // 상어사이즈 증가
count_eat = 0; // 먹은횟수 초기화
} else {
shark_size = move.size;
}
total_dist = move.dist; // 이동거리 업데이트
//printMap();
}
System.out.println(total_dist);
}
void inputData() throws Exception {
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader);
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
map = new int[N][N];
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j=0; j<N; j++) {
map[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Main m = new Main();
m.inputData(); // 입력 받는 부분
m.Solve();// 여기서부터 작성
}
}
<피드백>
1. 예외처리를 해줘야 하는 부분이 많아서 구현하는데 시간이 많이 걸렸다.
2. 아기상어 위치를 전역변수로 따로 저장한다는 생각을 못해서 통과를 못했다.
'알고리즘 PS > BFS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준] 7569번 - 토마토 (Java)(○) (0) | 2023.05.22 |
|---|---|
| [백준] 16954번 - 움직이는 미로 탈출 (Java)(○) (0) | 2023.03.13 |
| [백준] 7576번 - 토마토 (Java)(○) (0) | 2023.03.02 |
| [백준] 1525번 - 퍼즐 (Java)(△) (1) | 2022.12.20 |
| [백준] 2206번 - 벽 부수고 이동하기 (Java)(△) (0) | 2022.09.20 |




댓글